

Now, simply transfer all the data from the boot disk to the newly built RAID array and you are done. The next step is to replace the existing disk with scratch disks, then you need to restore and configure the RAID as a duplicate of the original. So here we go: connect all damaged disks to the boot disk and restore the contents to the disk. Keep in mind that this recovery should only be performed by professionals, as otherwise you may lose the entire array. Two working and preferably new disks to replace damaged disks.Install a UPS, router, backup PC or NAS, computer system for operations.
Purchase an external storage device with sufficient disk space (network attached storage (NAS) or personal computer).In order to use the manual method of recovering data from RAID 5 when two drives fail, you need to prepare:
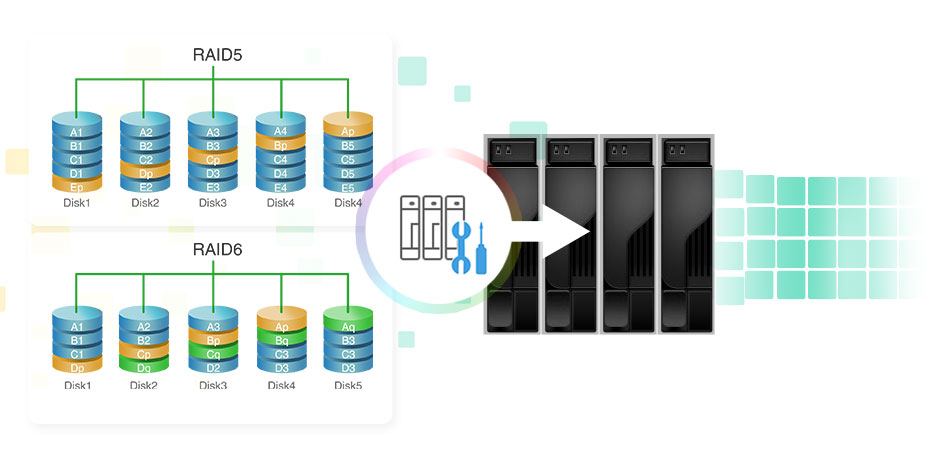
 Recently recovered data may be incomplete and differ from the original form. You should also take into account some of the nuances when recovering disks using this method: Now you should check the performance of the RAID array. Replace any damaged disks with new disks, test them for functionality, and then load the data onto the newly configured RAID. If possible, try restoring the backup to a different location, and if the data is clean and usable, proceed to the next step. Because of this, you should carefully consider the setup before you implement it.First you need to check if an available backup can be restored at all. Keep in mind that you can’t expand a striped set once it’s created. Once you create a striped set, users can use the set just like they would a normal drive. Create the volume as described previously under “Creating Volumes and Volume Sets.” The key difference is that you must select free space on three separate dynamic drives. Read the welcome page, and then click Next. In the Disk Management Graphical View, right-click an area marked Unallocated on a dynamic disk and then choose New Volume. In Disk Management, you can create a striped set with parity by completing the following steps: Creating a Striped Set with Parity in Disk Management If two disks fail, however, the parity information isn’t sufficient to recover the data and you’ll need to rebuild the striped set from backup. This process is called regenerating the striped set. If any of the drives in the striped set fails, the parity information can be used to recover the data. To allow for fault tolerance, RAID 5 writes parity checksums with the blocks of data.
Recently recovered data may be incomplete and differ from the original form. You should also take into account some of the nuances when recovering disks using this method: Now you should check the performance of the RAID array. Replace any damaged disks with new disks, test them for functionality, and then load the data onto the newly configured RAID. If possible, try restoring the backup to a different location, and if the data is clean and usable, proceed to the next step. Because of this, you should carefully consider the setup before you implement it.First you need to check if an available backup can be restored at all. Keep in mind that you can’t expand a striped set once it’s created. Once you create a striped set, users can use the set just like they would a normal drive. Create the volume as described previously under “Creating Volumes and Volume Sets.” The key difference is that you must select free space on three separate dynamic drives. Read the welcome page, and then click Next. In the Disk Management Graphical View, right-click an area marked Unallocated on a dynamic disk and then choose New Volume. In Disk Management, you can create a striped set with parity by completing the following steps: Creating a Striped Set with Parity in Disk Management If two disks fail, however, the parity information isn’t sufficient to recover the data and you’ll need to rebuild the striped set from backup. This process is called regenerating the striped set. If any of the drives in the striped set fails, the parity information can be used to recover the data. To allow for fault tolerance, RAID 5 writes parity checksums with the blocks of data.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
